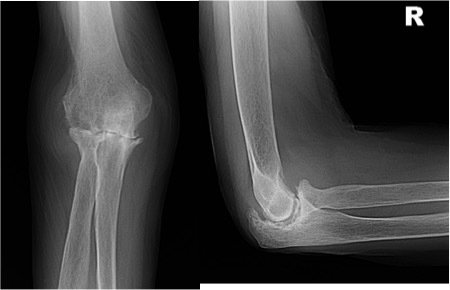
How is Elbow arthritis diagnosed?
A diagnosis of elbow arthritis is made based on the history of a gradual onset of pain in the elbow. Pain is usually aching in nature and experienced over the front or the back of the elbow. It is often associated with stiffness in the elbow and a feeling of roughness when moving the elbow. Some patients may experience pins and needles in the hand from irritation of the ulnar nerve. Examination shows painful restriction of movements of the elbow. An X-ray may demonstrate narrowing of the joint, erosion and formation of spurs. Special imaging with a CT scan or an MRI scan is sometimes necessary to aid in planning treatment.
How is Elbow arthritis treated?
In the early phase, pain may be controlled with activity modification and the use of pain relieving or anti-inflammatory medication.
Physiotherapy: You may be advised to see a physiotherapist to treat the stiffness and any associated muscle weakness.
Steroid injection: A steroid injection placed accurately into the joint may provide short-term pain relief. Injections should be avoided if surgery is being contemplated.
Visco-supplement injection: Hyaluronic acid is found in normal joint fluid and helps to lubricate the joint and remove by-products of inflammation. Synthetic hyaluronic acid is available for injection into the joint and may provide substantial relief from pain for a period of 3-6 months in patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. These injections are best performed under image guidance.
Arthroscopic Surgery: If symptoms persist despite adequate nonoperative treatment and if the arthritis is not severe, it may be appropriate to undertake arthroscopic treatment. This consists of “key-hole” surgery to remove loose fragments or bone spurs from the joint and release the tight capsule or sleeve of the joint. It may be necessary to decompress the ulnar nerve. Following surgery symptoms will usually improve over a period of time. For further information on surgical treatment, please refer to the section on “Arthroscopy for Bone spurs and Elbow Arthritis”.
Elbow replacement surgery: If the arthritis is advanced and the pain has failed to respond to other treatment measures, it may be appropriate to consider joint replacement surgery. Elbow replacements are successful at relieving pain and restoring function and quality of life. For further information please refer to the section on “Total elbow replacement”.