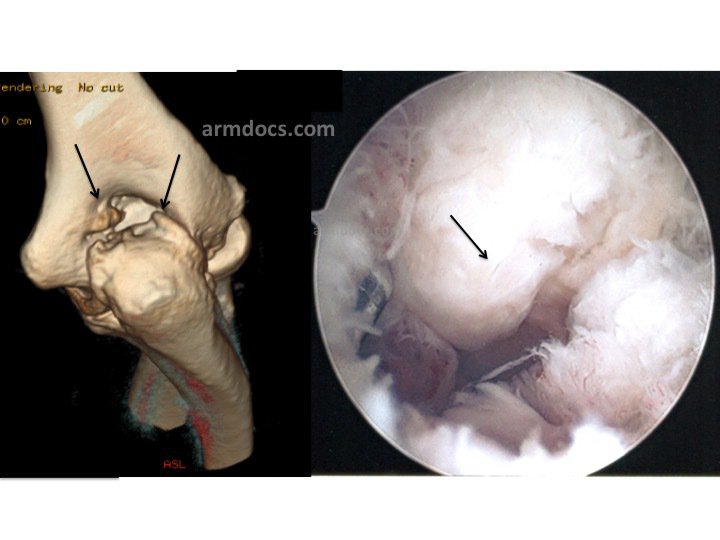
How are bone spurs of the elbow diagnosed?
Patients may experience difficulty reaching or in some instances feel pain at the end of the range of movements. Symptoms may interfere with the ability to work or participate in sports. Examination of the joint shows subtle loss of movement when compared to the opposite side (if normal). An X-ray may be performed to look for bone spurs and to assess the joint surfaces. Special imaging with an MRI or CT scan is often necessary to look at the bearing surface and identify the location of the bone spurs, to help plan the treatment.
How are bone spurs of the elbow treated?
If the symptoms are mild or infrequent, then modification of activities may be all that is required. If there is associated stiffness then physiotherapy may be of benefit. See the section on “Elbow stiffness”.
Surgery: In some patients, in whom symptoms are troublesome or interfere with sports or work, it may be appropriate to undertake surgical treatment. Surgery consists of arthroscopy (“key-hole” surgery) to remove bone spurs. If there are signs of joint stiffness as well then it may be necessary to release the thickened and scarred capsule or “sleeve” of the joint. For further information on surgical treatment, please refer to the section on “Arthroscopy for Bone spurs and Elbow arthritis”.